Understanding JavaScript prototype chain

|
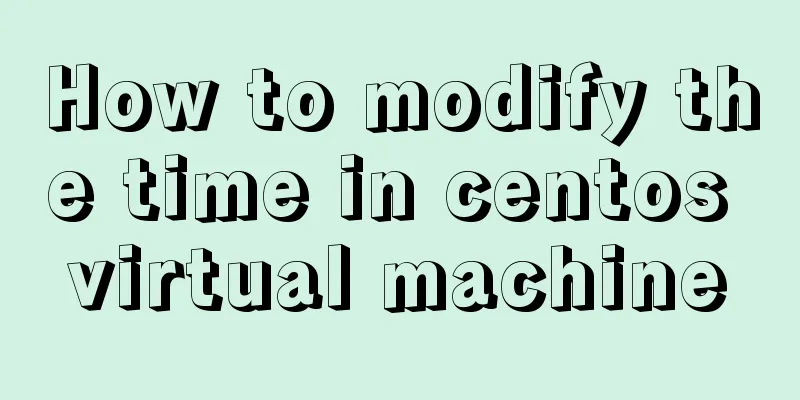
After reading this article, you will find that prototypes and prototype chains are so simple! The classic prototype chain equality diagram above, according to the following learning, you will easily master it. 1. Understanding the Equality Relationship between Prototype and Prototype ChainFirst of all, we need to understand two concepts clearly: Please read these two concepts three times with me and remember them. They will be used later. So what are
Please read these two concepts three times with me and remember them. They will be used later.
function Person(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.motherland = 'China'
let person01 = new Person('Xiaoming', 18);
The father of js followed the following two principles when designing js prototypes and prototype chains: Person.prototype.constructor == Person // **Guideline 1: The constructor of the prototype object (ie Person.prototype) points to the constructor itself** person01.__proto__ == Person.prototype // **Guideline 2: The __proto__ of the instance (ie person01) and the prototype object point to the same place** Please read these two rules three times with me and remember them. They will be used later. Remember the above four concepts and two criteria , any prototype chain equality judgment can be correct; You can check the above picture to see if you have understood the concept and criteria. Be sure to check the above picture. // Start analyzing this classic graph from the top function Foo() function Foo() let f1 = new Foo(); let f2 = new Foo(); f1.__proto__ = Foo.prototype; // Rule 2 f2.__proto__ = Foo.prototype; // Rule 2 Foo.prototype.__proto__ = Object.prototype; // Rule 2 (Foo.prototype is also a common object, so Rule 2 applies) Object.prototype.__proto__ = null; // The prototype chain stops here Foo.prototype.constructor = Foo; // Rule 1 Foo.__proto__ = Function.prototype; // Rule 2 Function.prototype.__proto__ = Object.prototype; // Principle 2 (Function.prototype is essentially a common object, so Principle 2 applies) Object.prototype.__proto__ = null; // The prototype chain stops here // **Note the difference between Foo and Function here, Foo is an instance of Function** // Start analyzing this classic graph from the middle Function Object() Function Object() let o1 = new Object(); let o2 = new Object(); o1.__proto__ = Object.prototype; // Rule 2 o2.__proto__ = Object.prototype; // Rule 2 Object.prototype.__proto__ = null; // The prototype chain stops here Object.prototype.constructor = Object; // Rule 1 Object.__proto__ = Function.prototype // Principle 2 (Object is essentially a function); // This is a bit confusing. Object is essentially a function, and Function is essentially an object. Function.prototype.__proto__ = Object.prototype; // Rule 2 (Function.prototype is also an ordinary object, so Rule 2 applies) Object.prototype.__proto__ = null; // The prototype chain stops here // Start analyzing this classic diagram from Function Function() below Function Function() Function.__proto__ = Function.prototype // Rule 2 Function.prototype.constructor = Function; // Rule 1 From this we can conclude that except for Object.prototype.__proto__ = null; Array.prototype.__proto__ = Object.prototype; Foo.prototype.__proto__ = Object.prototype; 2: What do prototypes and prototype chains mean?
Take console.log(person01) Print Let's create a person2 instance
let person02 = new Person('Xiaohua', 20);
console.log(person02)
Print
Person.prototype.hairColor = 'black';
Person.prototype.eat = function(){
console.log('We usually eat three meals a day.')
}
console.log(person01)
console.log(person02)
At this time, when we print
person01,hairColor = 'yellow'; console.log(person01) console.log(person02) It can be seen that This is the end of this article about understanding JS prototype prototype chain. For more relevant JS prototype prototype chain content, please search 123WORDPRESS.COM's previous articles or continue to browse the following related articles. I hope everyone will support 123WORDPRESS.COM in the future! You may also be interested in:
|
<<: Index Skip Scan in MySQL 8.0
>>: How to install Docker using scripts under Linux Centos
Recommend
Using react-virtualized to implement a long list of images with dynamic height
Table of contents Problems encountered during dev...
Example of using JS to determine whether an element is an array
Here are the types of data that can be verified l...
How to install Mysql5.7 in Centos6
environment Centos 6.6 MySQL 5.7 Install If the s...
Summary of Mysql update multi-table joint update method
Next, I will create two tables and execute a seri...
A brief talk about React Router's history
If you want to understand React Router, you shoul...
A brief discussion of several browser compatibility issues encountered
background Solving browser compatibility issues i...
HTML tbody usage
Structured Table (IExplore Only) 1) Group by rows ...
HTML Tutorial: Collection of commonly used HTML tags (5)
Related articles: Beginners learn some HTML tags ...
Nginx forward and reverse proxy and load balancing functions configuration code example
This article mainly introduces the configuration ...
Docker connection mongodb implementation process and code examples
After the container is started Log in to admin fi...
Detailed explanation of JavaScript private class fields and TypeScript private modifiers
Table of contents JavaScript private class fields...
Ubuntu 16.04 mysql5.7.17 open remote port 3306
Enable remote access to MySQL By default, MySQL u...
What should I do if I can't view the source file of a web page?
Q: Whether using Outlook or IE, when you right-cl...
Detailed explanation of Mysql communication protocol
1.Mysql connection method To understand the MySQL...
Tudou.com front-end overview
1. Division of labor and process <br />At T...