A brief discussion on whether CSS will block page rendering

|
Maybe everyone knows that js execution will block the parsing and rendering of the DOM tree, so will CSS loading block the parsing and rendering of the DOM tree? Next, let’s analyze it together. Principle Analysis So why does the above phenomenon occur? Let's analyze it from the browser's rendering process. Different browsers use different kernels, so their rendering processes are also different. There are currently two main WebKit rendering process
Gecko rendering process
From the two flowcharts above, we can see that the browser rendering process is as follows:
From the process we can see
DOMContentLoaded For browsers, there are two main events for page loading, one is DOMContentLoaded and the other is onLoad. There is nothing much to say about onLoad. It will only be triggered after all resources of the page are loaded. These resources include css, js, pictures, videos, etc. DOMContentLoaded, as the name implies, is triggered when the content of the page is parsed. Well, as we discussed above, css will block Dom rendering and js execution, and js will block Dom parsing. Then we can make the assumption that
Let's test the first case first:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>css blocking</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<script>
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function() {
console.log('DOMContentLoaded');
})
</script>
<link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/4.0.0-alpha.6/css/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
</body>
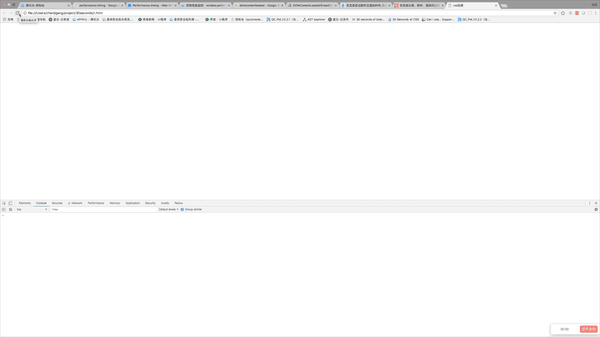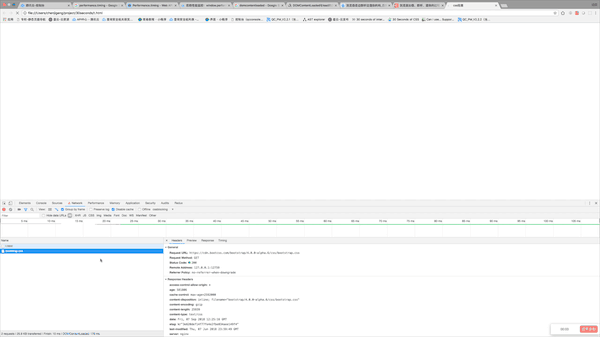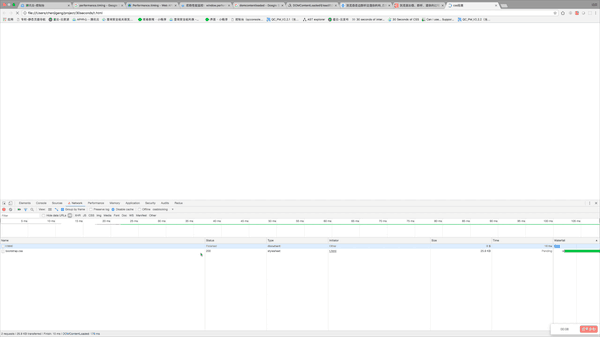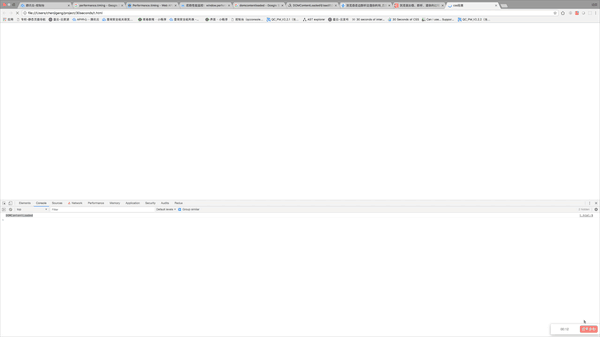
</html>The experimental results are as follows: From the animated picture we can see that the DOMContentLoaded event has been triggered before the css is loaded. Because there is no js code behind the css. Next, we will test the second case. It is very simple. Just add a line of code after the css.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>css blocking</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<script>
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function() {
console.log('DOMContentLoaded');
})
</script>
<link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/4.0.0-alpha.6/css/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script>
console.log('Is it my turn yet?');
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
We can see that the DOMContentLoaded event is triggered only after the css loading is complete. Therefore, we can conclude that:
Summarize From the above, we can draw the following conclusions:
Therefore, in order to avoid users seeing a long white screen time, we should increase the CSS loading speed as much as possible, such as using the following methods:
This is the end of this article on whether CSS will block page rendering. For more information about CSS blocking page rendering, please search for previous articles on 123WORDPRESS.COM or continue to browse the related articles below. I hope you will support 123WORDPRESS.COM in the future! |
<<: My CSS framework - base.css (reset browser default style)
>>: Details of watch monitoring properties in Vue
Recommend
Why the explain command may modify MySQL data
If someone asked you whether running EXPLAIN on a...
What the website needs most is to improve the experience of the target user group
"The great river flows eastward, the waves w...
How to connect Django 2.2 to MySQL database
1. The error information reported when running th...
How to install common components (mysql, redis) in Docker
Docker installs mysql docker search mysql Search ...
Detailed explanation of MySQL InnoDB index extension
Index extension: InnoDB automatically extends eac...
Summary of the three stages of visual designer growth
Many people have read this book: "Grow as a ...
Two ways to make IE6 display PNG-24 format images normally
Method 1: Please add the following code after <...
How to make ApacheBench support multi-url
Since the standard ab only supports stress testin...
Vue implements tab navigation bar and supports left and right sliding function
This article mainly introduces: using Vue to impl...
Tomcat9 download, installation and configuration + detailed tutorial on integrating into eclipse
tomcat official website tomcat is equivalent to a...
CSS3 uses scale() and rotate() to achieve zooming and rotation
1. scale() method Zoom refers to "reducing&q...
Use of vuex namespace
Table of contents Since Vuex uses a single state ...
Using zabbix to monitor the ogg process (Linux platform)
The ogg process of a database produced some time ...
Solution to 1449 and 1045 exceptions when connecting to MySQL
Solution to 1449 and 1045 exceptions when connect...
Vue implements paging function
This article example shares the specific code of ...











